On December 3, 2015 the U.S. Census Bureau released the 2010-2014 5 year ACS (American Community Survey) data. You can read all about it on the Census website. This fantastic five-year statistical database provides aggregate social and economic characteristics about American individuals and families down to the block group level. A number of online tools provide access to the ACS 2010-2014 data using graphical user interfaces (GUIs). These include the Census American FactFinder tool or via Social Explorer. The latter requires a subscription which UC Berkeley has and which is accessible to all folks with a CalNet login. Programmatic access to the data is possible via the Census API. In this blog post we will use the Census API to explore the ACS 2010-2014 data in the R statistical programming language.
It is not easy to work with Census data because of the size and the breadth of these data products. However, there are a number of packages that make it easier (but not easy!) to fetch, process and visualize Census data in R. These include the acs package by Ezra Glenn and the acs14lite package by Kyle Walker for downloading the ACS tabular data. The tigris package by Kyle Walker and Bob Rudis makes it relatively easy to download TIGER geographic boundary files, needed to map Census data, and link those boundaries to the ACS data. Hadley Wickham's popular and powerful ggplot2 package can be used to make static maps and charts of the data. The ggmap package allows you to create maps of Google Maps data and other online reference maps that can be used as basemaps for our plots. The CartoDB-R package by Virgilio Gómez-Rubio, which extends the work of Andrew Hill and Kyle Walker, makes it super easy to create online interactive maps of these data using the CartoDB.com APIs. The sp, rgdal and rgeos libraries are the workhorses of spatial data operations in R and are libraries upon which other packages may depend.
This tutorial has been tested with R version 3.2.2 (2015-08-14) on MacOSX 10.9.5. You may need to update your R to follow along. Ok, let's get started.
First, open RStudio or similar R development enviroment. Install the packages we will use if they are not already on your system. Some of these need to be installed with devtools which facilitaties installing packages that are not in a CRAN repository. You only do the package install once.
install.packages(c('dplyr','ggplot2','ggmap','sp','rgdal','rgeos','maptools','devtools'))
devtools::install_github('walkerke/acs14lite')
devtools::install_github('walkerke/tigris')
devtools::install_github('becarioprecario/cartodb-r/CartoDB', dep=TRUE)
Now load the libraries. A library is the code part of an R package which may also include documentation, data, and tests, etc.
library(sp) # for working with spatial data objects library(rgdal) # for importing and exporting spatial data in various formats library(acs14lite) # used to fetch ACS data library(tigris) # used to fetch TIGER data (shapefiles) library(dplyr) # used to reformat the ACS data library(maptools) # used by ggplot and base maps library(ggplot2) # used to make maps of the ACS data library(ggmap) # for adding Google Maps data to our maps library(CartoDB) # to create interactive maps in CartoDB.com
Set your working directory on your local computer
setwd('~/Documents/census') #mac style
#setwd("c:/docs/mydir") #windows os stye
my_census_api_key <- "your api key" set_api_key(my_census_api_key)
- B17021_001E: count of people for whom poverty status has been determined (the sample estimate)
- B17021_001M: count of people for whom poverty status has been determined (the margin of error)
- B17021_002E: count of those people whose income in the past 12 months is below poverty (estimate)
- B17021_002M: count of those people whose income in the past 12 months is below poverty (margin of error)
You can view these data in a web browser by putting the following URL in the address bar. Note, you will need to add your census API key
http://api.census.gov/data/2014/acs5?get=NAME,
B17021_001E,B17021_001M,B17021_002E,B17021_002M
&for=tract:*&in=state:06+county:075&key=YOUR_KEY
Fetching the ACS 2010 - 2014 Data
So now let's use the acs14lite R library to fetch ACS 2010-2014 poverty data for San Francisco census tracts. Available geographies for exploring an ACS variable with the acs14lite package include: 'us', 'region', 'division', 'state', 'county', 'tract', 'block group'. For package details enter ??acs14lite in the R console.
sf_poverty <- acs14(geography = 'tract', state = 'CA', county = 'San Francisco',
variable = c('B17021_001E', 'B17021_001M', 'B17021_002E', 'B17021_002M'))
head(sf_poverty) # view retrieved data
sf_poverty14 <- mutate(sf_poverty,
geoid = paste0(state, county, tract),
pctpov = round(100 * (B17021_002E / B17021_001E), 1),
moepov = round(100 * (moe_prop(B17021_002E, B17021_001E, B17021_002M, B17021_001M)),1))
sf_poverty14 <- select(sf_poverty14, geoid, pctpov, moepov)
head(sf_poverty14) # take a look at the retieved and reformatted ACS datasf_tracts <- tracts('CA', 'San Francisco', cb=TRUE)sf_tracts2 <- geo_join(sf_tracts, sf_poverty14, "GEOID", "geoid") sf_tracts2 <- sf_tracts2[!is.na(sf_tracts2$pctpov),] # look at the data class(sf_tracts2) str(sf_tracts2) str(sf_tracts2@data)
# First use fortify() to make the spatial data object a data frame that ggplot can map.
ggplotData <- fortify(sf_tracts2, data=sf_tracts2@data, region="geoid")
head(ggplotData) # look at the data frame created with the fortify function
# Join the ACS data to the fortified data frame
ggplotData <- merge(ggplotData, sf_tracts2@data, by.x="id", by.y="geoid")
head(ggplotData) # look at the data
# Plot the data to emphasize the areas of highest poverty
# First use the ggmap get_map function to fetch a Google Map image to use as our basemap
sf_basemap <-get_map('San Francisco', zoom=12)
ggmap(sf_basemap) +
geom_polygon(data = ggplotData, aes(x = long, y = lat, group = group, fill = pctpov), alpha=0.75) +
scale_fill_distiller(palette = "Reds") +
guides(fill = guide_legend(reverse = TRUE)) +
ggtitle("Percent of Individuals below Poverty Level\n ACS 2010-2014 Data") +
theme_nothing(legend=TRUE) +
coord_map()
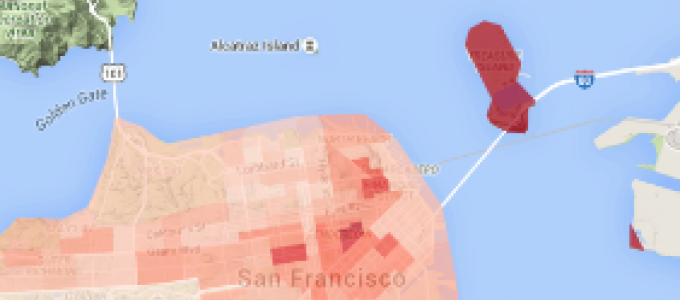
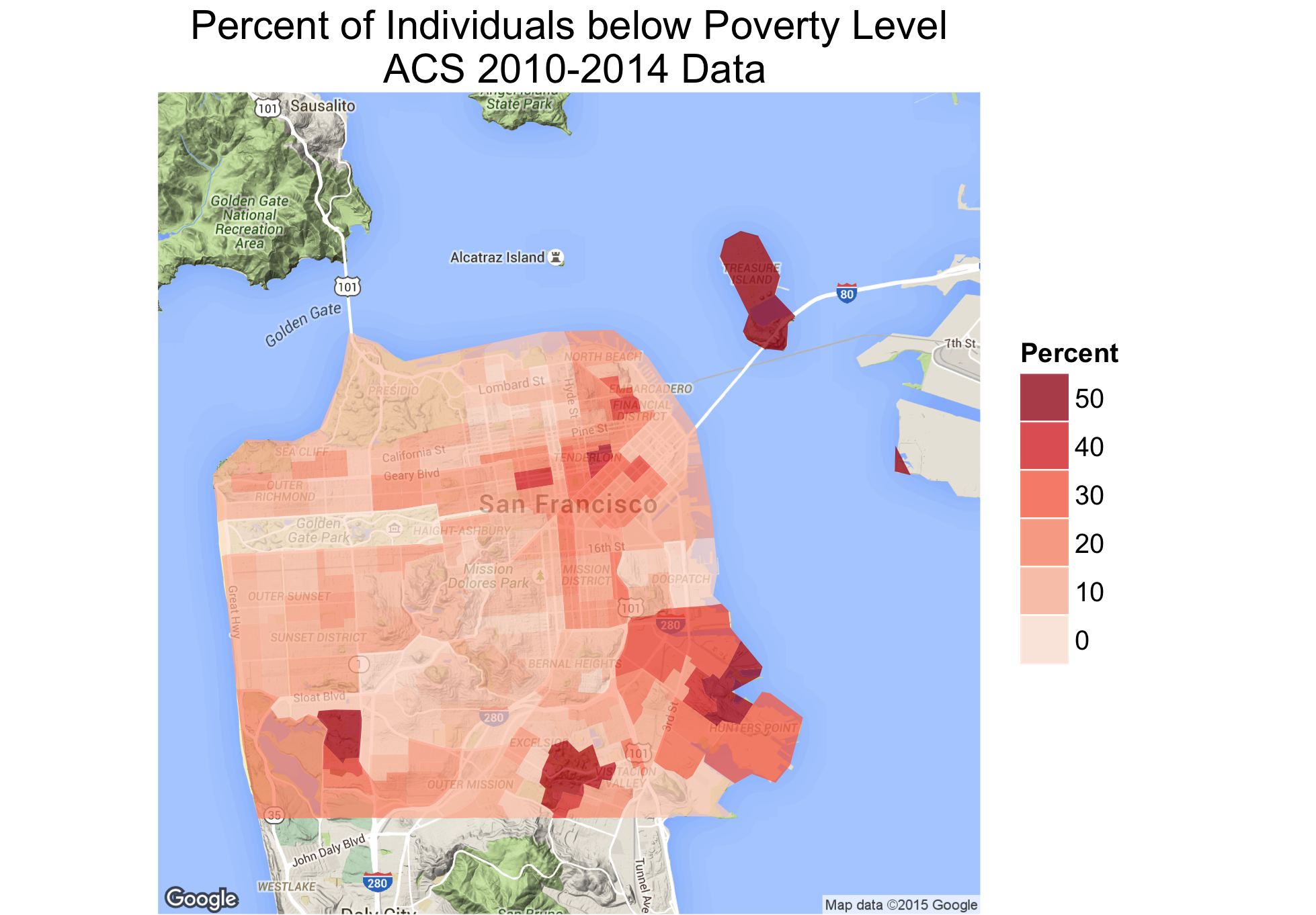
The code above creates the following map. To provide context, we used ggmap to create a basemap on which the ACS data is displayed. The ggplot and ggmap options are quite customizeable and powerful. However, the syntax can get a bit complicated, especially if you are unfamiliar with ggplot. You can use the package documentation to gain a better understanding of each function.
Mapping in CartoDB
If you don't want to dive into ggplot you can use an online mapping tool like CartoDB to create an interactive map of your ACS data. You need to first create a CartoDB account. When you login to your CartoDB account you can click on the heart icon to get your account user name and API Key. These are used to export your R spatial data object (here sf_tracts2) from R and import it into CartoDB. This process is shown below.
library(CartoDB) cdb_username <- 'your_username' cdb_apikey <- 'your_apikey' cartodb(cdb_username, cdb_apikey) r2cartodb(sf_tracts2, 'sf_poverty_by_tract')
- http://rpubs.com/walkerke/acs14lite
- https://rpubs.com/walkerke/tigris
- http://zevross.com/blog/2015/10/14/manipulating-and-mapping-us-census-da...